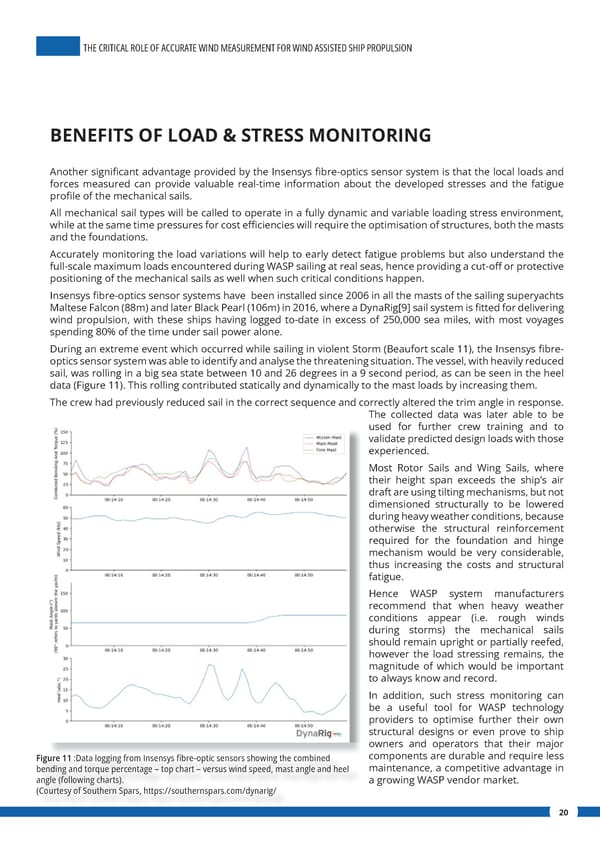
THE CRITICAL ROLE OF ACCURATE WIND MEASUREMENT FOR WIND ASSISTED SHIP PROPULSION BENEFITS OF LOAD & STRESS MONITORING Another signi昀椀cant advantage provided by the Insensys 昀椀bre-optics sensor system is that the local loads and forces measured can provide valuable real-time information about the developed stresses and the fatigue pro昀椀le of the mechanical sails. All mechanical sail types will be called to operate in a fully dynamic and variable loading stress environment, while at the same time pressures for cost e昀케ciencies will require the optimisation of structures, both the masts and the foundations. Accurately monitoring the load variations will help to early detect fatigue problems but also understand the full-scale maximum loads encountered during WASP sailing at real seas, hence providing a cut-o昀昀 or protective positioning of the mechanical sails as well when such critical conditions happen. Insensys 昀椀bre-optics sensor systems have been installed since 2006 in all the masts of the sailing superyachts Maltese Falcon (88m) and later Black Pearl (106m) in 2016, where a DynaRig[9] sail system is 昀椀tted for delivering wind propulsion, with these ships having logged to-date in excess of 250,000 sea miles, with most voyages spending 80% of the time under sail power alone. During an extreme event which occurred while sailing in violent Storm (Beaufort scale 11), the Insensys 昀椀bre- optics sensor system was able to identify and analyse the threatening situation. The vessel, with heavily reduced sail, was rolling in a big sea state between 10 and 26 degrees in a 9 second period, as can be seen in the heel data (Figure 11). This rolling contributed statically and dynamically to the mast loads by increasing them. The crew had previously reduced sail in the correct sequence and correctly altered the trim angle in response. The collected data was later able to be used for further crew training and to validate predicted design loads with those experienced. Most Rotor Sails and Wing Sails, where their height span exceeds the ship’s air draft are using tilting mechanisms, but not dimensioned structurally to be lowered during heavy weather conditions, because otherwise the structural reinforcement required for the foundation and hinge mechanism would be very considerable, thus increasing the costs and structural fatigue. Hence WASP system manufacturers recommend that when heavy weather conditions appear (i.e. rough winds during storms) the mechanical sails should remain upright or partially reefed, however the load stressing remains, the magnitude of which would be important to always know and record. In addition, such stress monitoring can be a useful tool for WASP technology providers to optimise further their own structural designs or even prove to ship owners and operators that their major Figure 11 :Data logging from Insensys 昀椀bre-optic sensors showing the combined components are durable and require less maintenance, a competitive advantage in bending and torque percentage – top chart – versus wind speed, mast angle and heel angle (following charts). a growing WASP vendor market. (Courtesy of Southern Spars, https://southernspars.com/dynarig/ 20
 The Critical Role of Accurate Wind Measurement for Wind Assisted Ship Propulsion Page 19 Page 21
The Critical Role of Accurate Wind Measurement for Wind Assisted Ship Propulsion Page 19 Page 21